|
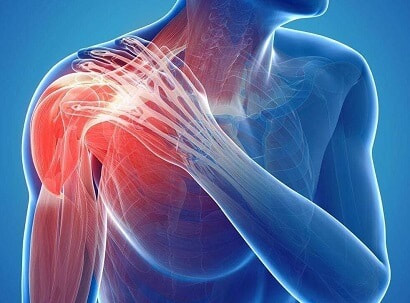
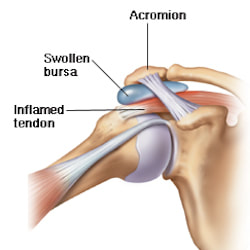
What is Bursitis? Bursitis is a condition that causes the small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae to become inflamed. A bursa is responsible for cushioning the tendons, ligaments, bones and muscles near the joint and preventing friction from occurring. This condition usually occurs in joints that are involved in repetitive movements, such as the shoulder, elbow, hip and knee. What are the symptoms? There are a range of symptoms that can present when bursitis has developed within the shoulder joint, including;
Causes of shoulder bursitis There are a number of potential causes but some of the most common can be a single injury such as a fall, repeated minor trauma like overuse injuries of the joint or muscles around the joint. When bursitis is caused from overuse injuries it is often associated with impingement and inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons as well. Prevention of shoulder bursitis Whilst it is difficult to determine singular causes in the development of bursitis there are a range of secondary factors that can contribute. Reducing causes of primary and secondary impingement are crucial in preventing shoulder bursitis and rotator cuff problems. Factors such as posture, muscle length, shoulder stability and rotator cuff strength can all contribute to the development of bursitis over time. Each of these factors can be optimised by completing specific exercises prescribed from a trained allied health professional. Treatment of shoulder bursitis
Shoulder bursitis is one of the most common shoulder injuries that presents in a range of populations. The rotator cuff muscles are responsible for the centralisation and stability of the shoulder joint. Adequate control within the shoulder then prevents injuries such as bursitis, impingement and dislocations. Interestingly, the arm only has one bony joint attachment where the collarbone meets the tip of the shoulder blade. The remainder of the shoulder joint attachment and stabilisers are all muscular, highlighting the importance of maintaining strength in the shoulder. Treatment for shoulder bursitis focuses on increasing range of movement in the shoulder joint without pain, regaining control of the shoulder blades, upper back and neck and improving strength in the rotator cuff and shoulder muscles. Each of these steps can take a number of weeks to successfully complete, so it is important to be patient and consistent during your treatment. If you suffer from shoulder bursitis, visit your local Accredited Exercise Physiologist who can help return your function and decrease pain! Written by, Aleisha Michael Accredited Exercise Physiologist.
0 Comments
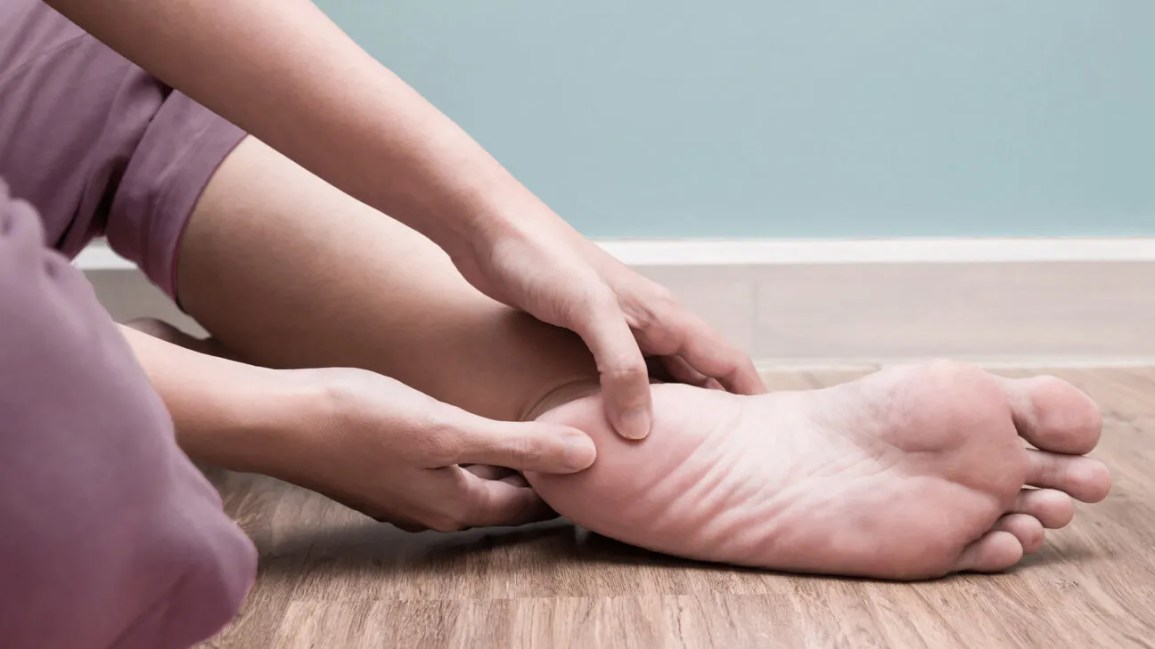
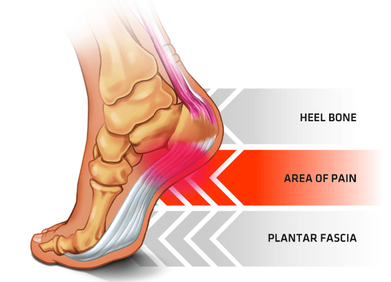
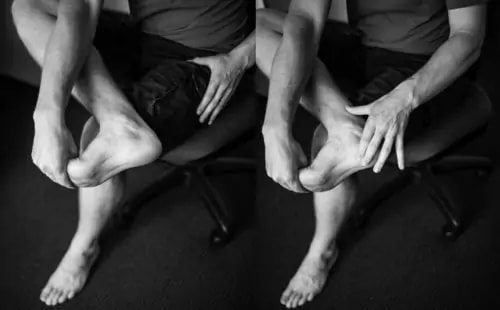
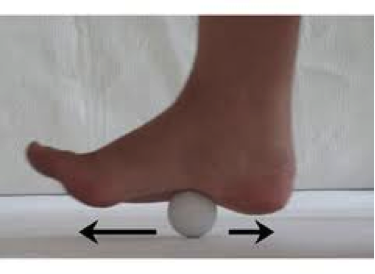
Plantar heel pain is something we see here in the clinic regularly and is something we have to be mindful of when prescribing exercise, particularly running or walking. Things that can increase your risk of plantar heel pain are overweight or obesity, a high increase in load such as running or walking and differing biomechanics of the leg and the foot (although this one is normally debated). What is plantar heel pain? Plantar heel pain is a term used to describe pain on the bottom of your foot near the heel. This umbrella term is sometimes used as it is debated as to whether the source of someone's foot pain can be determined. Terms like plantar fasciitis and plantar fasciopathy come under this umbrella term. Some experts use plantar heel pain prior to any ultrasound findings on the plantar fascia and before they can confidently diagnose plantar fasciopathy. Plantar fasciopathy is due to degeneration resulting from micro tears and necrosis of the plantar fascia through overuse and unsuitable loading. Unsuitable loading of the plantar fascia means the demand on the tissue structure from an activity or from increase in weight is larger than the plantar fascia can handle. Treatments There is a wide variety of treatments for plantar heel pain with a varying degree of positive effects. Some opt for more passive treatments like heel inserts, rest, ice and taping while others try and use more active strategies like activity modification, stretching and strengthening. The good thing about treatments for plantar heel pain is that many out perform a placebo or no treatment at all meaning that by doing something is beneficial. But what is the best? If something hurts then rest it right? Well unfortunately although this will give you some pain relief, this will not prevent any further pain in the future when you return to your activity. Rest may be required initially for pain relief but gradual activity modification (instead of complete rest) and optimal loading to improve the plantar fascia’s durability is going to be best for long term solutions. What does the research say It is widely known that stretching is one of the most beneficial treatments for plantar heel pain out there. Now however there is more evidence to suggest adding high slow resistance training can improve recovery even more. Advice and patient education is also key to helping people recover from plantar heel pain. Advice for people living with plantar heel pain (picture adopted from Dr Michael Rathleff research) If you have plantar heel pain and want to do something about it here are 3 strategies to try. Stretching (picture adopted from Dr Michael Rathleff research) Stretching prescribed here at the clinic is something that has been researched and proven effective. As seen in the picture above, grasp at the bottom of the toes on the bottom of the foot and pull your toes towards your shin bone until you can feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. Try this method 10 times for 10 seconds and try it 3 times a day. Rolling on a ball Using a similar mechanical method as stretching, rolling on a ball of any kind has been seen to have some positive benefits. Simply roll bare feet on a ball through the arch of your foot. The ball does not have to be a specific type of ball, any little ball will have an effect eg. cricket ball, golf ball and even a tennis ball. Try 5 times for 1 minute and try it 3 times a day Heavy Slow Resistance Training Strengthening has been proven to show significantly improved outcomes after the 3 month mark of rehabilitation compared to stretching. Here is how you would do it. As seen in the Video, use a towel so your toes are in a fully extended position on a step. Then perform a double leg or single leg calf raise slowly. It should take you 3 seconds to get to the top of the calf raise, staying for 2 seconds at the top and 3 seconds to return back down. Performing slowly will help to reduce any flair ups and increase time under tension. Try this exercise 12 reps x 3 sets with a weight you feel you could not lift any more than 12 times. Using books in a backpack is a good way to add weight. Single leg will be harder then double leg. When you feel you are getting stronger, Add more weight. An accessible level of pain to you is okay, however if your symptoms increase during the exercise or the next day, the load is too high. There is a quick review of what to do if you have plantar heel pain. It is only a guide and should not be taken as specific advice for you. If it is something you really want to get on top of, see one of our exercise physiologists. Izaac Boylan Accredited Exercise Physiologist So, you work in a physically demanding job and feel that this gets you enough physical activity throughout your day that you don’t need to do any extra, right?... WRONG. Whilst all this extra incidental activity throughout your day is giving you additional health benefits, it doesn’t give you the same BENEFITS as structured physical activity. What is the difference between incidental and structured physical activity? Incidental activity is defined as NON-PLANNED, UNSTRUCTURED ACTIVITY that accumulates in small portions over the course of a day. It can take many different forms including;
Whereas structured physical activity is PLANNED ACTIVITY that is completed in a continuous bout. This includes a planned walk, run or bike ride, gym sessions or classes or any other planned exercise session done individually or with others. Can I just do incidental activity? Whilst incidental activity provides many positive benefits it does not provide the same degree of benefit as structured physical activity. This is due to structured activity being completed in a continuous bout enabling our heart rate to increase, improving our cardiovascular and respiratory health. Completing specific strength training in planned exercise sessions also promotes a further increase in muscular strength and endurance when compared to incidental activity. Research has also shown that when activity is completed at a moderate intensity it assists in the prevention of a number of chronic conditions, including but not limited too;
What are the benefits of incidental activity?
By keeping your daily routine as active as possible there are a number of benefits that occur as well, such as;
So, what type of activity should I focus on? At the end of the day all movement counts and should be encouraged, whether it is a planned workout or sneaking a few extra steps in around the office! If you feel that you have been lacking with your structured physical activity recently, try adding in a few extra steps to your day by parking the car further away, taking the stairs instead of the lift or getting up from your chair once every hour! If you would like some more guidance about how to fit structured or incidental activity into your day try visiting an Accredited Exercise Physiologist! By, Aleisha Michael Accredited Exercise Physiologist. |
AuthorSLisa Parkinson Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed