|
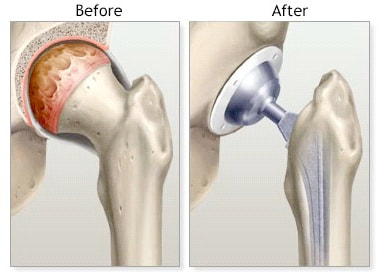
What does a total hip replacement involve? A total hip replacement is an operation that replaces damaged bone within the hip joint with prosthetic substitutes. The head or top of the thigh bone (femur) is replaced with a prosthetic head shaft and the socket of the hip joint where this head attaches is replaced with a synthetic bowl shaped surface. This promotes smooth movement between the thigh bone and pelvis and reduces pain or friction that may occur. When might a total hip replacement be needed?
A total hip replacement may be advised when there has been a fracture of the femur head caused from a fall or possible condition. Osteoporosis is often a large contributor to the high incidence of hip fractures in elderly individuals, due to the decreased bone mineral density it causes. A total hip replacement may also be recommended when degeneration from arthritis has occurred and in the joint making movement painful. If an individual suffers from regular hip dislocations or dysplasia it may also be an appropriate form of treatment. What are some of the risks involved with a total hip replacement? Only 2-10% of those who have a total hip replacement will experience complications during or after the surgery, including;
Importance of exercise Pre-Operative Developing a good foundation of muscular strength and stability around the affected hip is crucial before undergoing surgery. This not only increases the level of strength around the hip post-surgery but also promotes, decreased time spent in hospital post-surgery, improved recovery time and function, lowered anxiety levels, increased self-confidence and an improved quality of life and psychological health. Post-Operative The main aim of post-operative rehabilitation is to regain range of movement, strength, function and stability in the hip joint to return to daily activities. The surgery causes decreases in gluteal and quadriceps strength which needs to be retrained to ensure they can complete functional movements as soon as possible. This enables patients to regain the independence and increases their own confidence in their ability to complete tasks pain free. By, Aleisha Michael Accredited Exercise Physiologist.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSLisa Parkinson Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed